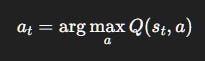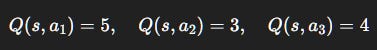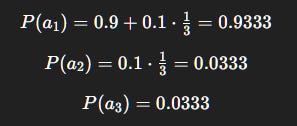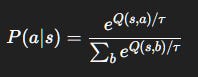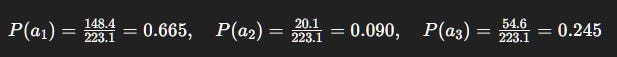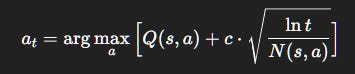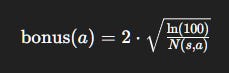Exploration vs Exploitation: The Eternal Dilemma in Reinforcement Learning
The Story: The Curious Tourist
Imagine you’re in Tokyo for the first time. Yesterday you discovered a fantastic sushi bar. You know exactly what you’ll get: fresh tuna, perfect rice, and happiness.
But across the street, there’s a neon-lit ramen shop you’ve never tried. It could be amazing … or a disaster.
This is the exploration vs exploitation dilemma:
Exploit: stick to the sushi bar (safe, known).
Explore: try ramen (unknown, risky, but maybe better long-term).
An RL agent faces this choice at every time step. Should it stick with what it knows, or explore something uncertain?
Step 1. Formalizing the Dilemma
At each time t, the agent has to select an action:
Exploitation (greed):
Always pick the best-known action.
Exploration (curiosity):
Choose randomly or probabilistically to try new actions.
Interpretation: Exploitation secures short-term certainty. Exploration risks short-term reward in exchange for information that may boost long-term return.
Visual:
Step 2. ε-Greedy Strategy: Controlled Coin Flip
The simplest balance is the ε-greedy policy:
With probability
ε, the agent explores.With probability 1 −
ε, it exploits the best-known action.
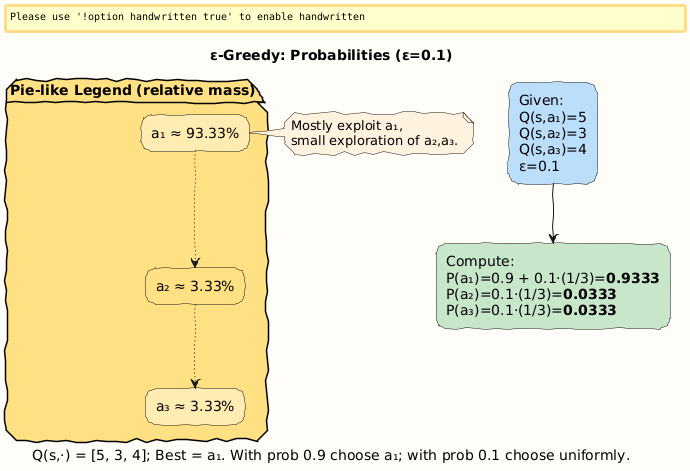
Numerical Example 1: ε-Greedy Probabilities
Suppose an agent in state s estimates:
Let ε = 0.1.
With 90% chance → pick
a_1.With 10% chance → pick uniformly among {
a_1,a_2,a_3}.
So probabilities:
Interpretation: The agent strongly favors a_1 (known best) but still occasionally tests a_2 and a_3. This avoids being “trapped” if the estimates are wrong.
Visual:
Step 3. Softmax Exploration: The Boltzmann Trick
ε-greedy treats all non-best actions equally. Softmax (a.k.a. Boltzmann) exploration is smarter:
τ(temperature) tunes randomness:High
τ: all actions ~ equal (exploration).Low
τ: greedy (exploitation).
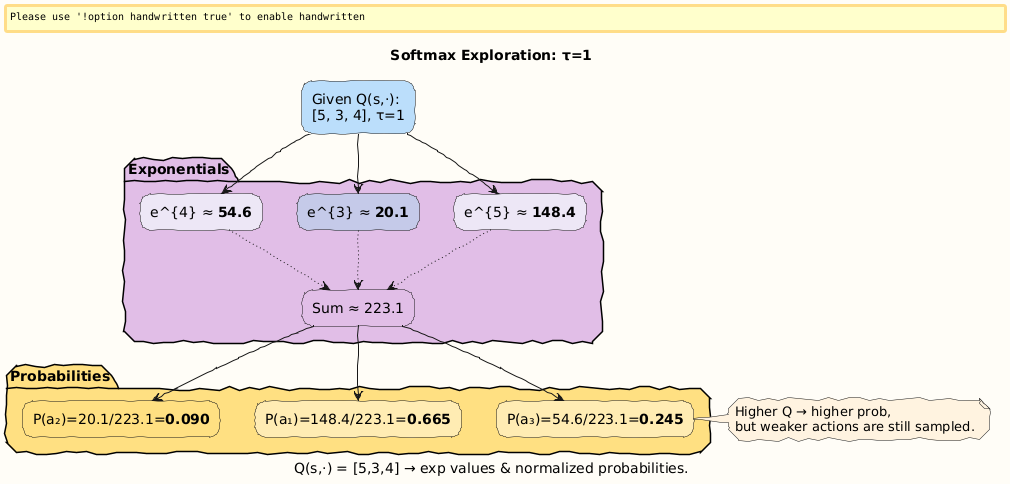
Numerical Example 2: Softmax Probabilities
Same Q-values: (5, 3, 4).
Let τ = 1. Compute exponentials:
e⁵≈ 148.4e³≈ 20.1e⁴≈ 54.6Sum = 223.1
So:
Interpretation: Unlike ε-greedy, softmax doesn’t treat all non-best equally. It assigns probability in proportion to estimated value. a_2 is weak but not ignored; a_3 has a decent chance.
Visual:
Step 4. Upper Confidence Bound (UCB): Optimism as a Strategy
A more sophisticated idea: explore when uncertain.
Choose actions based on:
Where:
N(s, a): how many times action aaa has been tried.c: exploration constant.ln t: ensures exploration fades as time grows.
The extra term is a bonus: actions with fewer trials get artificially inflated, forcing exploration.
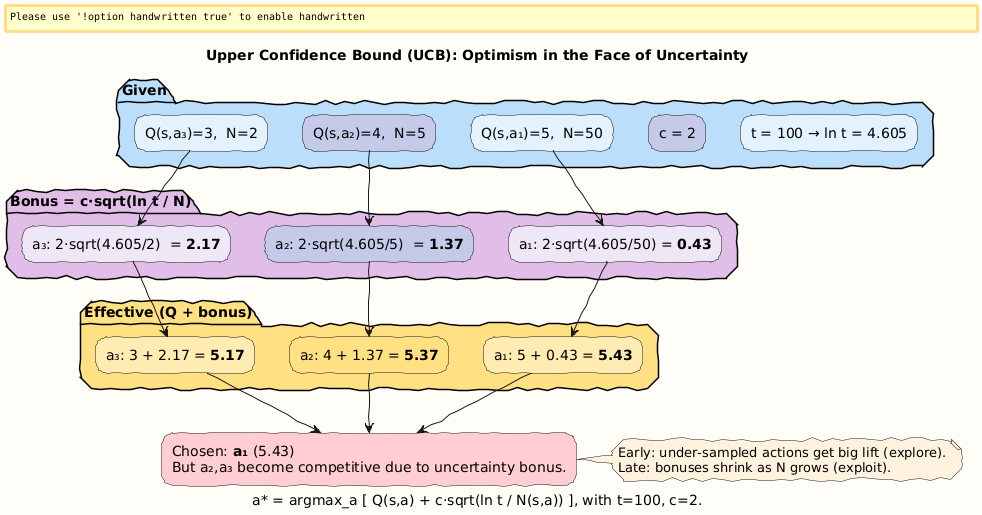
Numerical Example 3: UCB in Action
Suppose at time t = 100:
Q(s, a_1)= 5,N(s, a_1)= 50Q(s, a_2)= 4,N(s, a_2)= 5Q(s, a_3)= 3,N(s, a_3)= 2Let
c= 2.
Compute bonuses:
Effective values:
a_1= 5 + 0.43 = 5.43a_2= 4 + 1.37 = 5.37a_3= 3 + 2.17 = 5.17
Interpretation: Despite lower Q-values, a_2 and a_3 look competitive because of their uncertainty. The agent leans toward trying them.
Visual:
Importance of it: Exploration = Innovation
Chess: sacrifice short-term material to test new lines.
Science: experiments fail often, but exploration yields breakthroughs.
Business: R&D burns cash today but creates tomorrow’s unicorns.
RL agents mimic this universal lesson: curiosity is costly but necessary.
Special: Learn More in Learning to Learn: Reinforcement Learning Explained for Humans
If this balancing act excites you, and you want to see how ε-greedy, Softmax, and UCB connect to real-world RL training. I dive deep into it in my book:
Learning to Learn: Reinforcement Learning Explained for Humans
It combines:
Everyday analogies (like the sushi vs ramen story).
Mathematical depth (derivations of policies and bounds).
Worked problems (so you can calculate step by step, like we did here).
Bridges to advanced RL (policy gradients, actor–critic).
Grab your copy:
Closing
We formalized the exploration–exploitation dilemma.
We examined ε-greedy, Softmax, and UCB, with detailed numerical worked examples.
We saw how exploration strategies embody the principle: short-term sacrifice for long-term wisdom.
Next time → Q-Learning and Temporal Difference Learning, where these exploration strategies directly shape how agents learn optimal value functions.
Follow and Share
You can follow me on Medium to read more: https://medium.com/@satyamcser
#ReinforcementLearning #Exploration #Exploitation #EpsilonGreedy #Softmax #UCB #AIExplained #RLTraining #MLMath #satmis